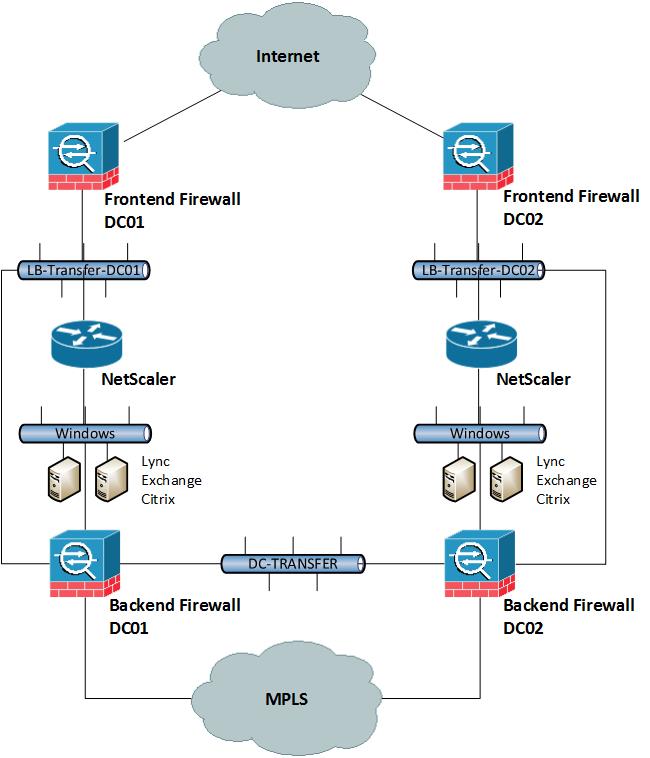
From my experience with Cisco ASAs over the last years it can make a big difference on the performance if the ASA is not correctly configured. You have to keep some things in mind when you install and set-up your firewalls. Of course for low traffic networks it will not make a big difference but for data centre infrastructures it can make a huge difference on the load of your CPU.
In the end from the network perspective everything can influence the performance: throughput (bit/s, packets/s and packet size), sessions (new and max connections), inspection and encryption (VPN). I recommend to have a look at the CiscoLive 365 presentation from 2012 – Maximizing Firewall Performance, very interesting presentation about the ASA hardware platform’s and what influence the performance.
At first some general information about the ASA platform’s before you start configuring
ASA5510 to 5550
- On-board interfaces are better for higher packet rate
ASA5580
- Traffic distribution over both I/O bridges
- Keep flows on same I/O bridge and place interface pairs on the same card (inside and outside)
ASA55xx-X
- Possible to use jumbo frames but only make sense in end-to-end configuration
All ASA platform’s
- Use port-channel for 1Gbit interfaces to split frames over multiple FIFO queues and RX rings (10Gbit interface have four RX rings)
- Avoid inter-context traffic because it uses the loopback buffer
SNMP and Logging settings
Disable SNMP traps if not needed and use polling only
snmp-server host INSIDE 10.255.0.10 poll community public version 2c
Only use one syslog server and proper trap level to reduce CPU overhead also adjust the ASDM logging
logging enable
logging host INSIDE 10.255.0.10
logging trap critical
logging history errors
logging queue 2048
logging asdm warning
logging asdm-buffer-size 512
asdm history enable
Filter logging messages to reduce CPU overhead and prevent misconfigured debug logging to overload the CPU of the firewall
:: Build TCP Connection
no logging message 302013
:: Teardown TCP Connection
no logging message 302014
:: Deny udp reverse path check
no logging message 106021
:: Bad TCP hdr length
no logging message 500003
:: Denied ICMP type=0, no matching session
no logging message 313004
:: No matching connection for ICMP error message
no logging message 313005
:: Inbound TCP connection denied outside Firewall Access
no logging message 106001
:: Inbount UDP connection denied outside Firewall Access
no logging message 106006
no logging message 106007
Disable Threat Detection statistics
threat-detection basic-threat
no threat-detection statistics
Enable threat detection statistics only temporary because it can have a big impact on the performance of your ASA but keep basic threat detection always enabled!
ICMP interface settings
Not really related to optimizing the performance but ICMP should be correctly configured
icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1
icmp permit any echo OUTSIDE
icmp permit any echo-reply OUTSIDE
icmp permit any unreachable OUTSIDE
icmp permit any echo INSIDE
icmp permit any echo-reply INSIDE
icmp permit any unreachable INSIDE
Transport Protocol settings
Adjust default TCP MMS (Maximum Segment Size) 1380 to higher value (Please be careful sometimes it makes sense to leave it at 1380).
sysopt connection tcpmss 1460
sysopt connection tcpmss minimum 0
ASA silently drop packets without sending TCP reset.
no service resetinbound
no service resetoutside
Timeout value settings
Change timeout values for XLATE table, TCP/UDP sessions and Firewall Engine settings
timeout xlate 1:05:00
timeout udp 00:01:00
timeout conn 01:00:00
timeout half-closed 00:10:00
timeout h323 00:00:01
timeout sunrpc 00:01:00
timeout sip 00:05:00
timeout sip_media 00:01:00
timeout h225 00:00:01
timeout mgcp 00:00:01
timeout uauth 00:00:01 absolute
Antispoofing Options
ip verify reverse-path interface OUTSIDE
ip verify reverse-path interface INSIDE
Modular Policy Framework (MPF)
Modular Policy Framework provides a consistent and flexible way to configure security appliance features. For example, you can use Modular Policy Framework to create a timeout configuration that is specific to a particular TCP application, as opposed to one that applies to all TCP applications.
ACL and Class-Map for unrestricted IP traffic between backend networks
access-list UNRESTRICTED-IP-TRAFFIC extended permit ip object NET_10.1.100.0 object NET_10.2.100.0
access-list UNRESTRICTED-IP-TRAFFIC extended permit ip object NET_10.1.200.0 object NET_10.2.200.0
access-list UNRESTRICTED-IP-TRAFFIC extended permit ip object NET_10.1.300.0 object NET_10.2.300.0
class-map unrestricted-ip-traffic
match access-list UNRESTRICTED-IP-TRAFFIC
exit
ACL and Class-Map for any IP traffic
access-list ALL-IP-TRAFFIC extended permit ip any any
class-map all-ip-traffic
match access-list ALL-IP-TRAFFIC
exit
Inspection Policy for DNS traffic
policy-map type inspect dns custom_dns_map
parameters
message-length maximum 1280
dns-guard
protocol-enforcement
no nat-rewrite
no id-randomization
no tsig enforced
no id-mismatch
exit
exit
Policy Map
Turn off not needed inspection to reduce processing overhead within the CPU. In the policy map you define the TCP connection quotas for the before configured class-map’s ACLs.
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect icmp
inspect icmp error
inspect ftp
inspect dns custom_dns_map
no inspect rtsp
no inspect pptp
no inspect sip
no inspect ctiqbe
no inspect esmtp
no inspect gtp
no inspect h323
no inspect h323 ras
no inspect h323 h225
no inspect http
no inspect ils
no inspect mgcp
no inspect netbios
no inspect rsh
no inspect skinny
no inspect snmp
no inspect sqlnet
no inspect sunrpc
no inspect tftp
no inspect xdmcp
exit
class unrestricted-ip-traffic
set connection advanced-options tcp-state-bypass
set connection per-client-max 0
set connection conn-max 0
set connection timeout embryonic 0:00:10
set connection timeout half-closed 0:10:00
set connection timeout tcp 1:00:00
exit
class all-ip-traffic
set connection random-sequence-number enable
set connection per-client-max 500
set connection conn-max 0
set connection embryonic-conn-max 100
set connection per-client-embryonic-max 50
set connection timeout embryonic 0:00:10
set connection timeout half-closed 0:10:00
set connection timeout tcp 1:00:00
exit
exit
Additional information
There are also some more points to think about what can influense the performance of the ASA firewall.
- Several smaller ACLs are better than a large one (ACL size mostly impacts conn setup rate)
- Static NAT entries are best for higher performance
- Optimize dynamic routing because it has an impact on the CPU
- Careful with inline packet capturing
- Keep HTTP conn replication disabled for best performance results
- Share the load with active virtual contexts on each firewall, see here my post: Cisco ASA Virtual Context Mode