In the Kubernetes/OpenShift community everyone is talking about Istio service mesh, so I wanted to share my experience about the installation and running a sample microservice application with Istio on OpenShift 3.11 and 4.0. Service mesh on OpenShift is still at least a few month away from being available generally to run in production but this gives you the possibility to start testing and exploring Istio. I have found good documentation about installing Istio on OCP and OKD have a look for more information.
To install Istio on OpenShift 3.11 you need to apply the node and master prerequisites you see below; for OpenShift 4.0 and above you can skip these steps and go directly to the istio-operator installation:
sudo bash -c 'cat << EOF > /etc/origin/master/master-config.patch
admissionConfig:
pluginConfig:
MutatingAdmissionWebhook:
configuration:
apiVersion: apiserver.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kubeConfigFile: /dev/null
kind: WebhookAdmission
ValidatingAdmissionWebhook:
configuration:
apiVersion: apiserver.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kubeConfigFile: /dev/null
kind: WebhookAdmission
EOF'
sudo cp -p /etc/origin/master/master-config.yaml /etc/origin/master/master-config.yaml.prepatch
sudo bash -c 'oc ex config patch /etc/origin/master/master-config.yaml.prepatch -p "$(cat /etc/origin/master/master-config.patch)" > /etc/origin/master/master-config.yaml'
sudo su -
master-restart api
master-restart controllers
exit
sudo bash -c 'cat << EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/99-elasticsearch.conf
vm.max_map_count = 262144
EOF'
sudo sysctl vm.max_map_count=262144
The Istio installation is straight forward by starting first to install the istio-operator:
oc new-project istio-operator oc new-app -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Maistra/openshift-ansible/maistra-0.9/istio/istio_community_operator_template.yaml --param=OPENSHIFT_ISTIO_MASTER_PUBLIC_URL=<-master-public-hostname->
Verify the operator deployment:
oc logs -n istio-operator $(oc -n istio-operator get pods -l name=istio-operator --output=jsonpath={.items..metadata.name})
Once the operator is running we can start deploying Istio components by creating a custom resource:
cat << EOF > ./istio-installation.yaml apiVersion: "istio.openshift.com/v1alpha1" kind: "Installation" metadata: name: "istio-installation" namespace: istio-operator EOF oc create -n istio-operator -f ./istio-installation.yaml
Check and watch the Istio installation progress which might take a while to complete:
oc get pods -n istio-system -w # The installation of the core components is finished when you see: ... openshift-ansible-istio-installer-job-cnw72 0/1 Completed 0 4m
Afterwards, to finish off the Istio installation, we need to install the Kiali web console:
bash <(curl -L https://git.io/getLatestKialiOperator) oc get route -n istio-system -l app=kiali
Verifying that all Istio components are running:
$ oc get pods -n istio-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE elasticsearch-0 1/1 Running 0 9m grafana-74b5796d94-4ll5d 1/1 Running 0 9m istio-citadel-db879c7f8-kfxfk 1/1 Running 0 11m istio-egressgateway-6d78858d89-58lsd 1/1 Running 0 11m istio-galley-6ff54d9586-8r7cl 1/1 Running 0 11m istio-ingressgateway-5dcf9fdf4b-4fjj5 1/1 Running 0 11m istio-pilot-7ccf64f659-ghh7d 2/2 Running 0 11m istio-policy-6c86656499-v45zr 2/2 Running 3 11m istio-sidecar-injector-6f696b8495-8qqjt 1/1 Running 0 11m istio-telemetry-686f78b66b-v7ljf 2/2 Running 3 11m jaeger-agent-k4tpz 1/1 Running 0 9m jaeger-collector-64bc5678dd-wlknc 1/1 Running 0 9m jaeger-query-776d4d754b-8z47d 1/1 Running 0 9m kiali-5fd946b855-7lw2h 1/1 Running 0 2m openshift-ansible-istio-installer-job-cnw72 0/1 Completed 0 13m prometheus-75b849445c-l7rlr 1/1 Running 0 11m
Let’s start to deploy the microservice application example by using the Google Hipster Shop, it contains multiple microservices which is great to test with Istio:
# Create new project oc new-project hipster-shop # Set permissions to allow Istio to deploy the Envoy-Proxy side-car container oc adm policy add-scc-to-user anyuid -z default -n hipster-shop oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged -z default -n hipster-shop # Create Hipster Shop deployments and Istio services oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/berndonline/openshift-ansible/master/examples/istio-hipster-shop.yml oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/berndonline/openshift-ansible/master/examples/istio-manifest.yml # Wait and check that all pods are running before creating the load generator oc get pods -n hipster-shop -w # Create load generator deployment oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/berndonline/openshift-ansible/master/examples/istio-loadgenerator.yml
As you see below each pod has a sidecar container with the Istio Envoy proxy which handles pod traffic:
[centos@ip-172-26-1-167 ~]$ oc get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE adservice-7894dbfd8c-g4m9v 2/2 Running 0 49m cartservice-758d66c648-79fj4 2/2 Running 4 49m checkoutservice-7b9dc8b755-h2b2v 2/2 Running 0 49m currencyservice-7b5c5f48fc-gtm9x 2/2 Running 0 49m emailservice-79578566bb-jvwbw 2/2 Running 0 49m frontend-6497c5f748-5fc4f 2/2 Running 0 49m loadgenerator-764c5547fc-sw6mg 2/2 Running 0 40m paymentservice-6b989d657c-klp4d 2/2 Running 0 49m productcatalogservice-5bfbf4c77c-cw676 2/2 Running 0 49m recommendationservice-c947d84b5-svbk8 2/2 Running 0 49m redis-cart-79d84748cf-cvg86 2/2 Running 0 49m shippingservice-6ccb7d8ff7-66v8m 2/2 Running 0 49m [centos@ip-172-26-1-167 ~]$
The Kiali web console answers the question about what microservices are part of the service mesh and how are they connected which gives you a great level of detail about the traffic flows:
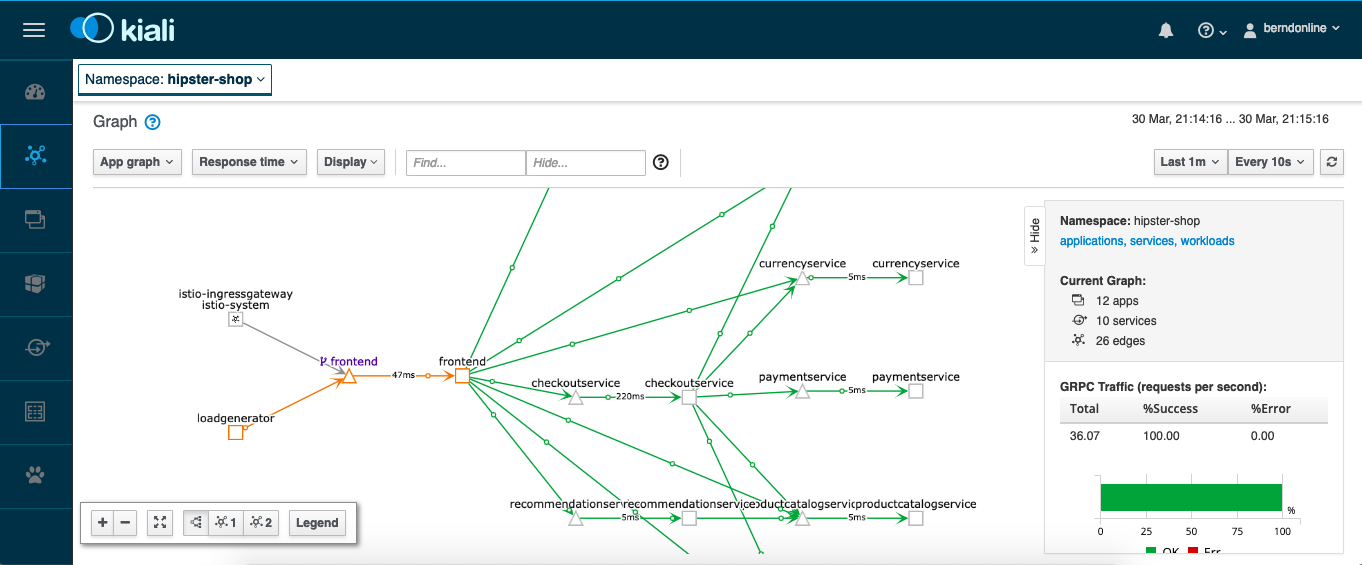
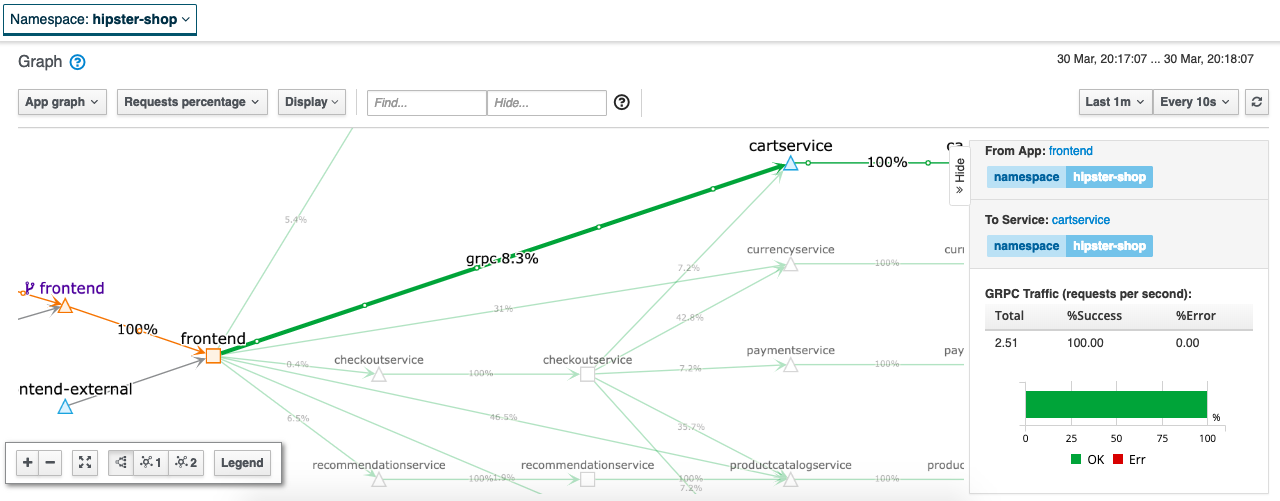
Detailed traffic flow view:
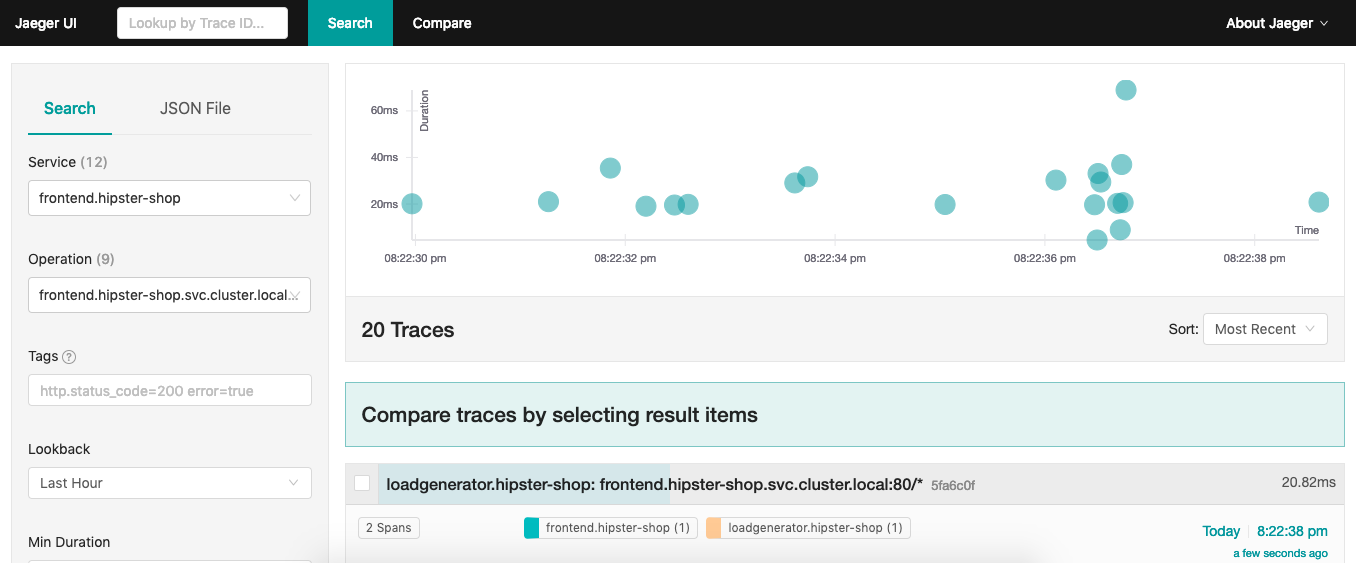
The Isito installation comes with Jaeger which is an open source tracing tool to monitor and troubleshoot transactions:
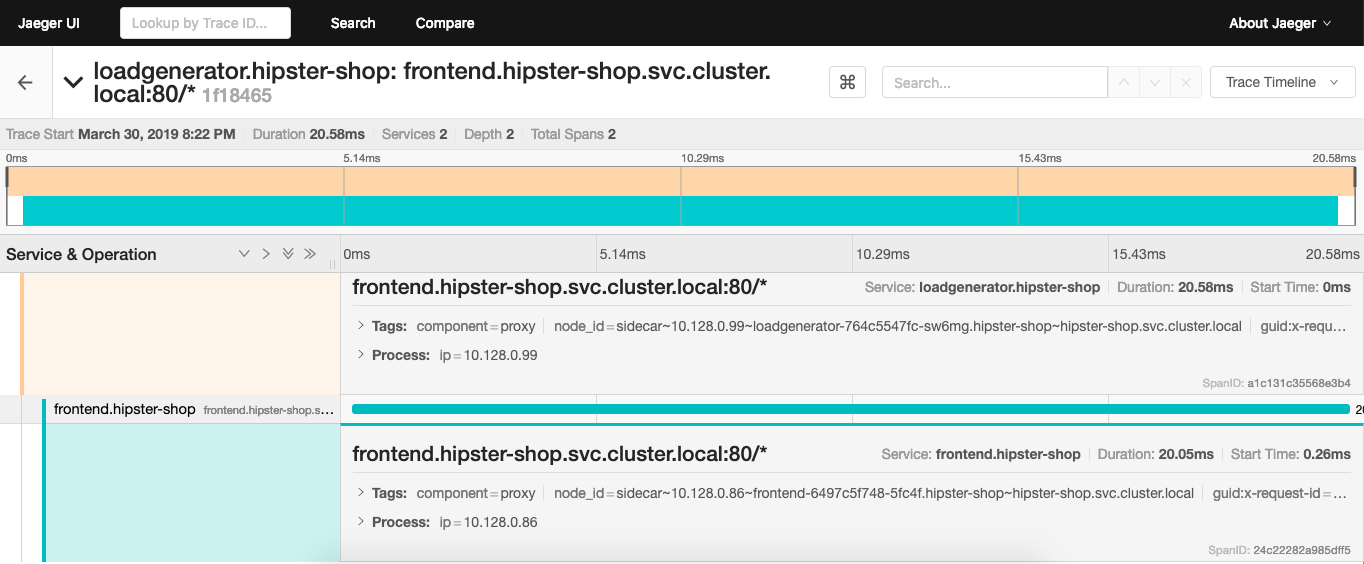
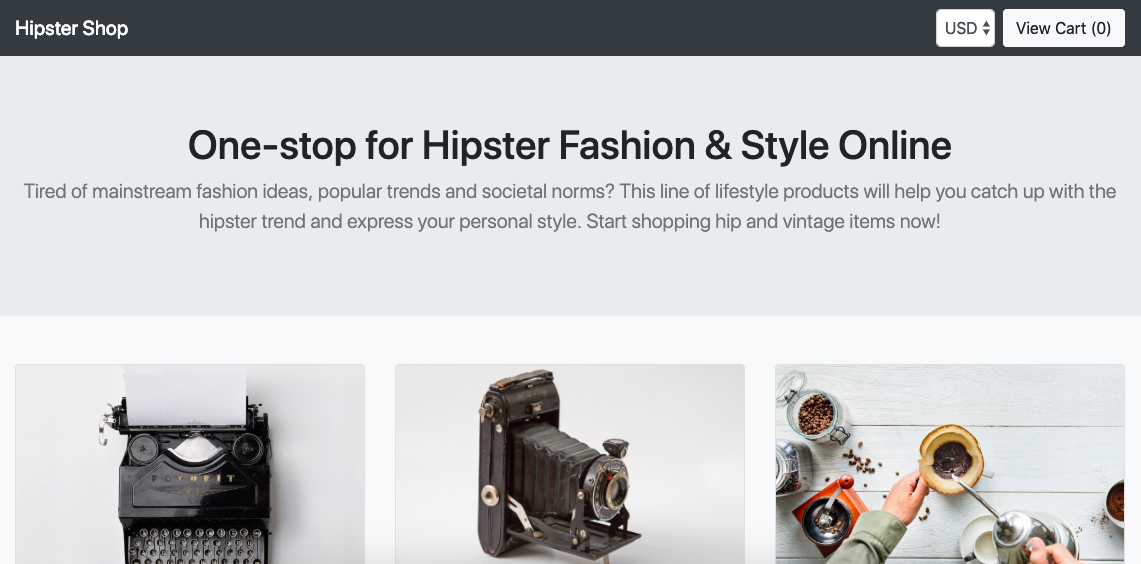
Enough about this, lets connect to our cool Hipster Shop and happy shopping:
Additionally there is another example, the Istio Bookinfo if you want to try something smaller and less complex:
oc new-project myproject
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user anyuid -z default -n myproject
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged -z default -n myproject
oc apply -n myproject -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Maistra/bookinfo/master/bookinfo.yaml
oc apply -n myproject -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Maistra/bookinfo/master/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
export GATEWAY_URL=$(oc get route -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}')
curl -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$GATEWAY_URL/productpage
curl -o destination-rule-all.yaml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.0/samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml
oc apply -f destination-rule-all.yaml
curl -o destination-rule-all-mtls.yaml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.0/samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all-mtls.yaml
oc apply -f destination-rule-all-mtls.yaml
oc get destinationrules -o yaml
I hope this is a useful article for getting started with Istio service mesh on OpenShift.