The concept of a single-node or All-in-One OpenShift / Kubernetes cluster isn’t something new, years ago when I was working with OpenShift 3 and before that with native Kubernetes, we were using single-node clusters as ephemeral development environment, integrations testing for pull-request or platform releases. It was only annoying because this required complex Jenkins pipelines, provision the node first, then install prerequisites and run the openshift-ansible installer playbook. Not always reliable and not a great experience but it done the job.
This is possible as well with the new OpenShift/OKD 4 version and with the help from OpenShift Hive. The experience is more reliable and quicker than previously and I don’t need to worry about de-provisioning, I will let Hive delete the cluster after a few hours automatically.
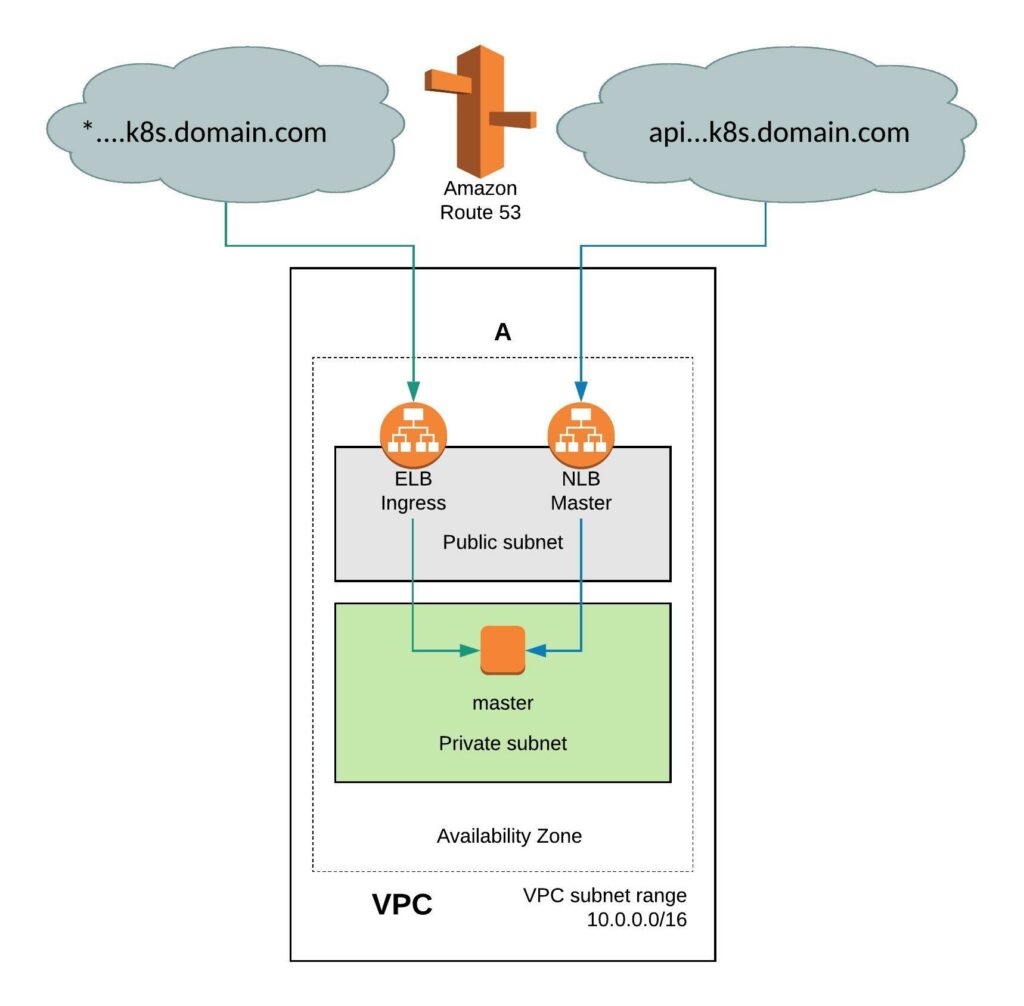 It requires a few simple modifications in the install-config. You need to add the Availability Zone you want where the instance will be created. When doing this the VPC will only have two subnets, one public and one private subnet in eu-west-1. You can also install the single-node cluster into an existing VPC you just have to specify subnet ids. Change the compute worker node replicas zero and control-plane replicas to one. Make sure to have an instance size with enough CPU and memory for all OpenShift components because they need to fit onto the single node. The rest of the install-config is pretty much standard.
It requires a few simple modifications in the install-config. You need to add the Availability Zone you want where the instance will be created. When doing this the VPC will only have two subnets, one public and one private subnet in eu-west-1. You can also install the single-node cluster into an existing VPC you just have to specify subnet ids. Change the compute worker node replicas zero and control-plane replicas to one. Make sure to have an instance size with enough CPU and memory for all OpenShift components because they need to fit onto the single node. The rest of the install-config is pretty much standard.
---
apiVersion: v1
baseDomain: k8s.domain.com
compute:
- name: worker
platform:
aws:
zones:
- eu-west-1a
rootVolume:
iops: 100
size: 22
type: gp2
type: r4.xlarge
replicas: 0
controlPlane:
name: master
platform:
aws:
zones:
- eu-west-1a
rootVolume:
iops: 100
size: 22
type: gp2
type: r5.2xlarge
replicas: 1
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: okd-aio
networking:
clusterNetwork:
- cidr: 10.128.0.0/14
hostPrefix: 23
machineCIDR: 10.0.0.0/16
networkType: OpenShiftSDN
serviceNetwork:
- 172.30.0.0/16
platform:
aws:
region: eu-west-1
pullSecret: ""
sshKey: ""
Create a new install-config secret for the cluster.
kubectl create secret generic install-config-aio -n okd --from-file=install-config.yaml=./install-config-aio.yaml
We will be using OpenShift Hive for the cluster deployment because the provision is more simplified and Hive can also apply any configuration using SyncSets or SelectorSyncSets which is needed. Add the annotation hive.openshift.io/delete-after: “2h” and Hive will automatically delete the cluster after 4 hours.
---
apiVersion: hive.openshift.io/v1
kind: ClusterDeployment
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
annotations:
hive.openshift.io/delete-after: "2h"
name: okd-aio
namespace: okd
spec:
baseDomain: k8s.domain.com
clusterName: okd-aio
controlPlaneConfig:
servingCertificates: {}
installed: false
platform:
aws:
credentialsSecretRef:
name: aws-creds
region: eu-west-1
provisioning:
releaseImage: quay.io/openshift/okd:4.5.0-0.okd-2020-07-14-153706-ga
installConfigSecretRef:
name: install-config-aio
pullSecretRef:
name: pull-secret
sshKey:
name: ssh-key
status:
clusterVersionStatus:
availableUpdates: null
desired:
force: false
image: ""
version: ""
observedGeneration: 0
versionHash: ""
Apply the cluster deployment to your clusters namespace.
kubectl apply -f ./clusterdeployment-aio.yaml
This is slightly faster than provision 6 nodes cluster and will take around 30mins until your ephemeral test cluster is ready to use.