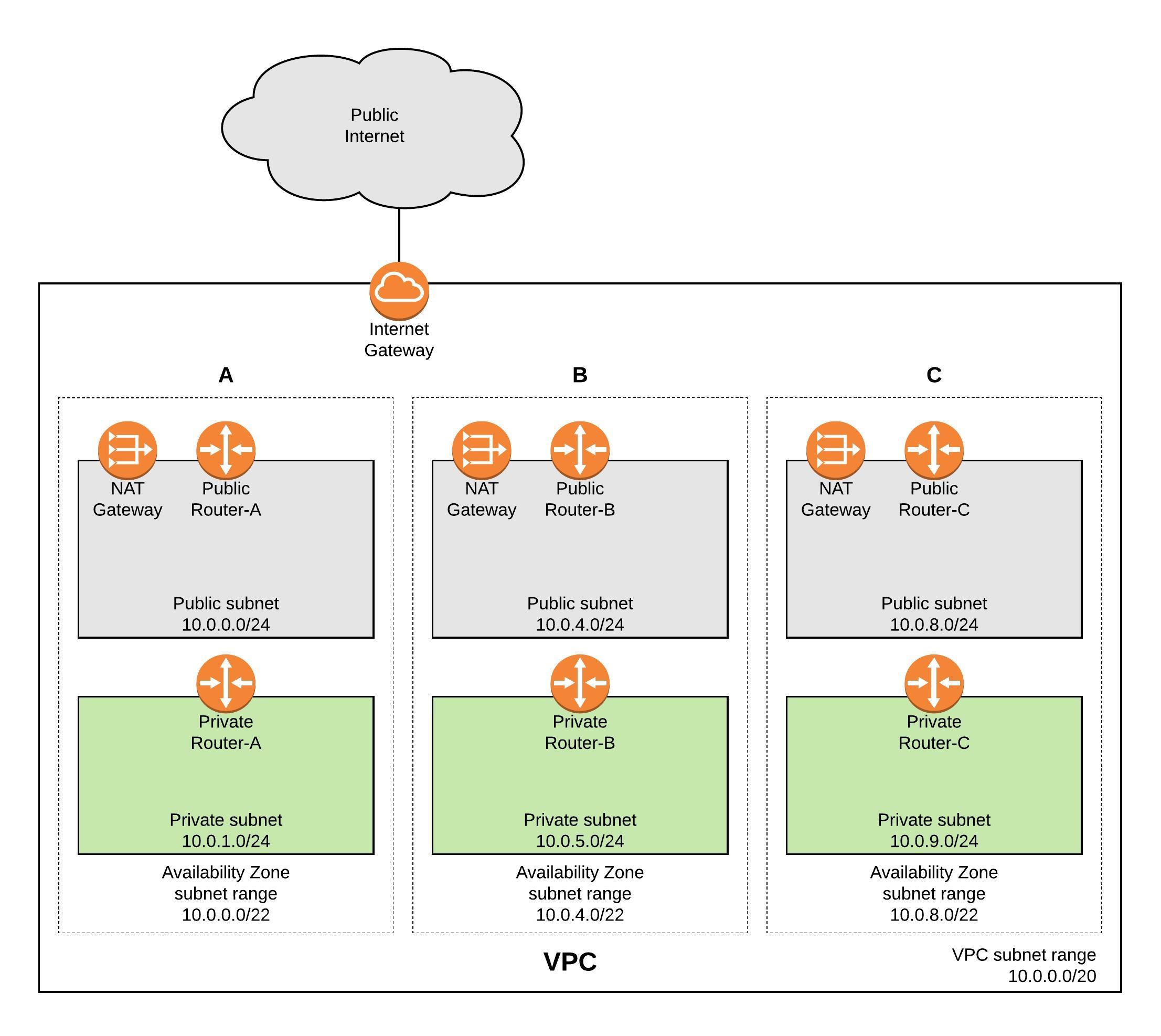
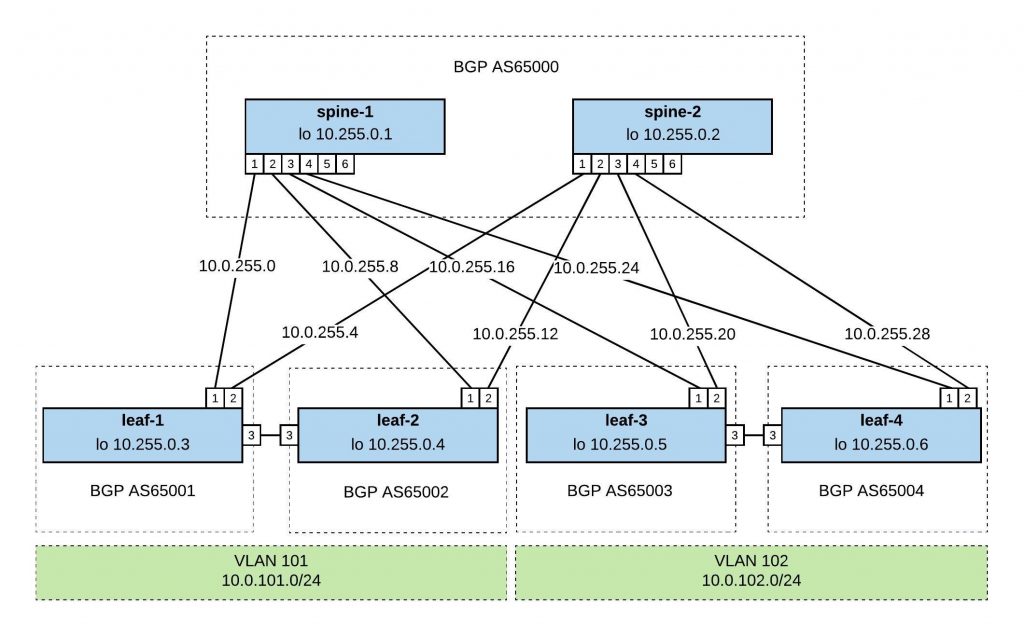
Before I start deploying the AWS VPC with HashCorp’s Terraform I want to explain the design of the Virtual Private Cloud. The main focus here is primarily for redundancy to ensure that if one Availability Zone (AZ) becomes unavailable that it is not interrupting the traffic and causing outages in your network, the NAT Gateway for example run per AZ so you need to make sure that these services are spread over multiple AZs.
AWS VPC network overview:
Before you start using Terraform you need to install the binary and it is also very useful to install the AWS command line interface. Please don’t forget to register the AWS CLI and add access and secure key.
pip install awscli --upgrade --user wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.11.7/terraform_0.11.7_linux_amd64.zip unzip terraform_0.11.7_linux_amd64.zip sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin/
Terraform is a great product and creates infrastructure as code, and is independent from any cloud provider so there is no need to use AWS CloudFormation like in my example. My repository for the Terraform files can be found here: https://github.com/berndonline/aws-terraform
Let’s start with the variables file, which defines the needed settings for deploying the VPC. Basically you only need to change the variables to deploy the VPC to another AWS region:
...
variable "aws_region" {
description = "AWS region to launch servers."
default = "eu-west-1"
}
...
variable "vpc_cidr" {
default = "10.0.0.0/20"
description = "the vpc cdir range"
}
variable "public_subnet_a" {
default = "10.0.0.0/24"
description = "Public subnet AZ A"
}
variable "public_subnet_b" {
default = "10.0.4.0/24"
description = "Public subnet AZ A"
}
variable "public_subnet_c" {
default = "10.0.8.0/24"
description = "Public subnet AZ A"
}
...
The vpc.tf file is the Terraform template which deploys the private and public subnets, the internet gateway, multiple NAT gateways and the different routing tables and adds the needed routes towards the internet:
# Create a VPC to launch our instances into
resource "aws_vpc" "default" {
cidr_block = "${var.vpc_cidr}"
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
tags {
Name = "VPC"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "PublicSubnetA" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.default.id}"
cidr_block = "${var.public_subnet_a}"
tags {
Name = "Public Subnet A"
}
availability_zone = "${data.aws_availability_zones.available.names[0]}"
}
...
In the main.tf you define which provider to use:
# Specify the provider and access details
provider "aws" {
region = "${var.aws_region}"
}
# Declare the data source
data "aws_availability_zones" "available" {}
Now let’s start deploying the environment, first you need to initialise Terraform “terraform init“:
berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$ terraform init Initializing provider plugins... - Checking for available provider plugins on https://releases.hashicorp.com... - Downloading plugin for provider "aws" (1.25.0)... The following providers do not have any version constraints in configuration, so the latest version was installed. To prevent automatic upgrades to new major versions that may contain breaking changes, it is recommended to add version = "..." constraints to the corresponding provider blocks in configuration, with the constraint strings suggested below. * provider.aws: version = "~> 1.25" Terraform has been successfully initialized! You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands should now work. If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform, rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary. berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$
Next, let’s do a dry run “terraform plan” to see all changes Terraform would apply:
berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$ terraform plan
Refreshing Terraform state in-memory prior to plan...
The refreshed state will be used to calculate this plan, but will not be
persisted to local or remote state storage.
data.aws_availability_zones.available: Refreshing state...
------------------------------------------------------------------------
An execution plan has been generated and is shown below.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
+ aws_eip.natgw_a
id:
allocation_id:
association_id:
domain:
instance:
network_interface:
private_ip:
public_ip:
vpc: "true"
...
+ aws_vpc.default
id:
assign_generated_ipv6_cidr_block: "false"
cidr_block: "10.0.0.0/20"
default_network_acl_id:
default_route_table_id:
default_security_group_id:
dhcp_options_id:
enable_classiclink:
enable_classiclink_dns_support:
enable_dns_hostnames: "true"
enable_dns_support: "true"
instance_tenancy: "default"
ipv6_association_id:
ipv6_cidr_block:
main_route_table_id:
tags.%: "1"
tags.Name: "VPC"
Plan: 27 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: You didn't specify an "-out" parameter to save this plan, so Terraform
can't guarantee that exactly these actions will be performed if
"terraform apply" is subsequently run.
berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$
Because nothing is deployed, Terraform would apply 27 changes, so let’s do this by running “terraform apply“. Terraform will check the state and will ask you to confirm and then apply the changes:
berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$ terraform apply
data.aws_availability_zones.available: Refreshing state...
An execution plan has been generated and is shown below.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
+ aws_eip.natgw_a
id:
allocation_id:
association_id:
domain:
instance:
network_interface:
private_ip:
public_ip:
vpc: "true"
...
+ aws_vpc.default
id:
assign_generated_ipv6_cidr_block: "false"
cidr_block: "10.0.0.0/20"
default_network_acl_id:
default_route_table_id:
default_security_group_id:
dhcp_options_id:
enable_classiclink:
enable_classiclink_dns_support:
enable_dns_hostnames: "true"
enable_dns_support: "true"
instance_tenancy: "default"
ipv6_association_id:
ipv6_cidr_block:
main_route_table_id:
tags.%: "1"
tags.Name: "VPC"
Plan: 27 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
aws_eip.natgw_c: Creating...
allocation_id: "" => ""
association_id: "" => ""
domain: "" => ""
instance: "" => ""
network_interface: "" => ""
private_ip: "" => ""
public_ip: "" => ""
vpc: "" => "true"
aws_eip.natgw_a: Creating...
allocation_id: "" => ""
association_id: "" => ""
domain: "" => ""
instance: "" => ""
network_interface: "" => ""
private_ip: "" => ""
public_ip: "" => ""
vpc: "" => "true"
...
aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetB: Creation complete after 0s (ID: rtbassoc-174ba16c)
aws_nat_gateway.public_nat_c: Still creating... (1m40s elapsed)
aws_nat_gateway.public_nat_c: Still creating... (1m50s elapsed)
aws_nat_gateway.public_nat_c: Creation complete after 1m56s (ID: nat-093319a1fa62c3eda)
aws_route_table.private_route_c: Creating...
propagating_vgws.#: "" => ""
route.#: "" => "1"
route.4170986711.cidr_block: "" => "0.0.0.0/0"
route.4170986711.egress_only_gateway_id: "" => ""
route.4170986711.gateway_id: "" => ""
route.4170986711.instance_id: "" => ""
route.4170986711.ipv6_cidr_block: "" => ""
route.4170986711.nat_gateway_id: "" => "nat-093319a1fa62c3eda"
route.4170986711.network_interface_id: "" => ""
route.4170986711.vpc_peering_connection_id: "" => ""
tags.%: "" => "1"
tags.Name: "" => "Private Route C"
vpc_id: "" => "vpc-fdffb19b"
aws_route_table.private_route_c: Creation complete after 1s (ID: rtb-d64632af)
aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetC: Creating...
route_table_id: "" => "rtb-d64632af"
subnet_id: "" => "subnet-17da194d"
aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetC: Creation complete after 1s (ID: rtbassoc-35749e4e)
Apply complete! Resources: 27 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$
Terraform successfully applied all the changes so let’s have a quick look in the AWS web console:
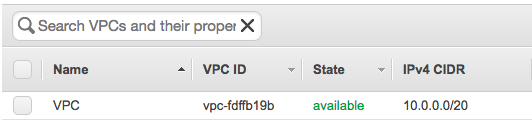
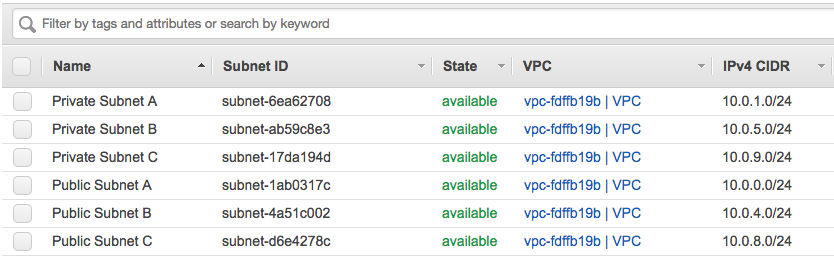
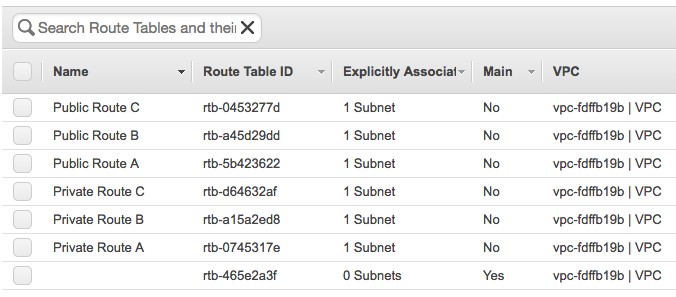
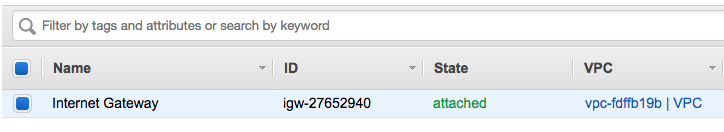
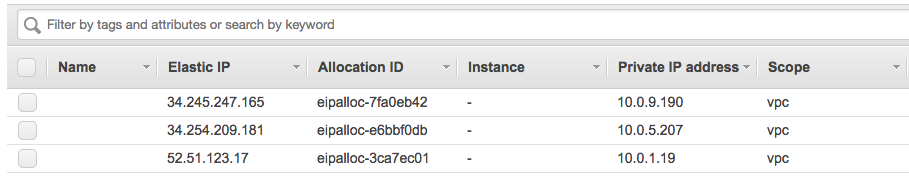
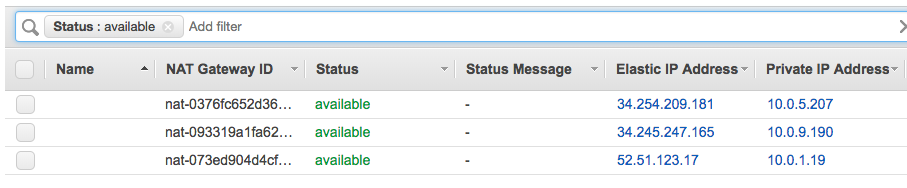
You can change the environment and run “terraform apply” again and Terraform would deploy the changes you have made. In my example below I didn’t, so Terraform would do nothing because it tracks the state that is deployed and that I have defined in the vpc.tf:
berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$ terraform apply aws_eip.natgw_c: Refreshing state... (ID: eipalloc-7fa0eb42) aws_vpc.default: Refreshing state... (ID: vpc-fdffb19b) aws_eip.natgw_a: Refreshing state... (ID: eipalloc-3ca7ec01) aws_eip.natgw_b: Refreshing state... (ID: eipalloc-e6bbf0db) data.aws_availability_zones.available: Refreshing state... aws_subnet.PublicSubnetC: Refreshing state... (ID: subnet-d6e4278c) aws_subnet.PrivateSubnetC: Refreshing state... (ID: subnet-17da194d) aws_subnet.PrivateSubnetA: Refreshing state... (ID: subnet-6ea62708) aws_subnet.PublicSubnetA: Refreshing state... (ID: subnet-1ab0317c) aws_network_acl.all: Refreshing state... (ID: acl-c75f9ebe) aws_internet_gateway.gw: Refreshing state... (ID: igw-27652940) aws_subnet.PrivateSubnetB: Refreshing state... (ID: subnet-ab59c8e3) aws_subnet.PublicSubnetB: Refreshing state... (ID: subnet-4a51c002) aws_route_table.public_route_b: Refreshing state... (ID: rtb-a45d29dd) aws_route_table.public_route_a: Refreshing state... (ID: rtb-5b423622) aws_route_table.public_route_c: Refreshing state... (ID: rtb-0453277d) aws_nat_gateway.public_nat_b: Refreshing state... (ID: nat-0376fc652d362a3b1) aws_nat_gateway.public_nat_a: Refreshing state... (ID: nat-073ed904d4cf2d30e) aws_route_table_association.PublicSubnetA: Refreshing state... (ID: rtbassoc-b14ba1ca) aws_route_table_association.PublicSubnetB: Refreshing state... (ID: rtbassoc-277d975c) aws_route_table.private_route_a: Refreshing state... (ID: rtb-0745317e) aws_route_table.private_route_b: Refreshing state... (ID: rtb-a15a2ed8) aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetB: Refreshing state... (ID: rtbassoc-174ba16c) aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetA: Refreshing state... (ID: rtbassoc-60759f1b) aws_nat_gateway.public_nat_c: Refreshing state... (ID: nat-093319a1fa62c3eda) aws_route_table_association.PublicSubnetC: Refreshing state... (ID: rtbassoc-307e944b) aws_route_table.private_route_c: Refreshing state... (ID: rtb-d64632af) aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetC: Refreshing state... (ID: rtbassoc-35749e4e) Apply complete! Resources: 0 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed. berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$
To remove the environment use run “terraform destroy“:
berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$ terraform destroy aws_eip.natgw_c: Refreshing state... (ID: eipalloc-7fa0eb42) data.aws_availability_zones.available: Refreshing state... aws_eip.natgw_a: Refreshing state... (ID: eipalloc-3ca7ec01) aws_vpc.default: Refreshing state... (ID: vpc-fdffb19b) aws_eip.natgw_b: Refreshing state... (ID: eipalloc-e6bbf0db) ... An execution plan has been generated and is shown below. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols: - destroy Terraform will perform the following actions: - aws_eip.natgw_a - aws_eip.natgw_b - aws_eip.natgw_c ... Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 27 to destroy. Do you really want to destroy? Terraform will destroy all your managed infrastructure, as shown above. There is no undo. Only 'yes' will be accepted to confirm. Enter a value: yes aws_network_acl.all: Destroying... (ID: acl-c75f9ebe) aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetA: Destroying... (ID: rtbassoc-60759f1b) aws_route_table_association.PublicSubnetC: Destroying... (ID: rtbassoc-307e944b) aws_route_table_association.PublicSubnetA: Destroying... (ID: rtbassoc-b14ba1ca) aws_route_table_association.PublicSubnetB: Destroying... (ID: rtbassoc-277d975c) aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetC: Destroying... (ID: rtbassoc-35749e4e) aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetB: Destroying... (ID: rtbassoc-174ba16c) aws_route_table_association.PrivateSubnetB: Destruction complete after 0s ... aws_internet_gateway.gw: Destroying... (ID: igw-27652940) aws_eip.natgw_c: Destroying... (ID: eipalloc-7fa0eb42) aws_subnet.PrivateSubnetC: Destroying... (ID: subnet-17da194d) aws_subnet.PrivateSubnetC: Destruction complete after 1s aws_eip.natgw_c: Destruction complete after 1s aws_internet_gateway.gw: Still destroying... (ID: igw-27652940, 10s elapsed) aws_internet_gateway.gw: Destruction complete after 11s aws_vpc.default: Destroying... (ID: vpc-fdffb19b) aws_vpc.default: Destruction complete after 0s Destroy complete! Resources: 27 destroyed. berndonline@lab:~/aws-terraform$
I hope this article was informative and explains how to deploy a VPC with Terraform. In the coming weeks I will add additional functions like deploying EC2 Instances and Load Balancing.
Please share your feedback and leave a comment.
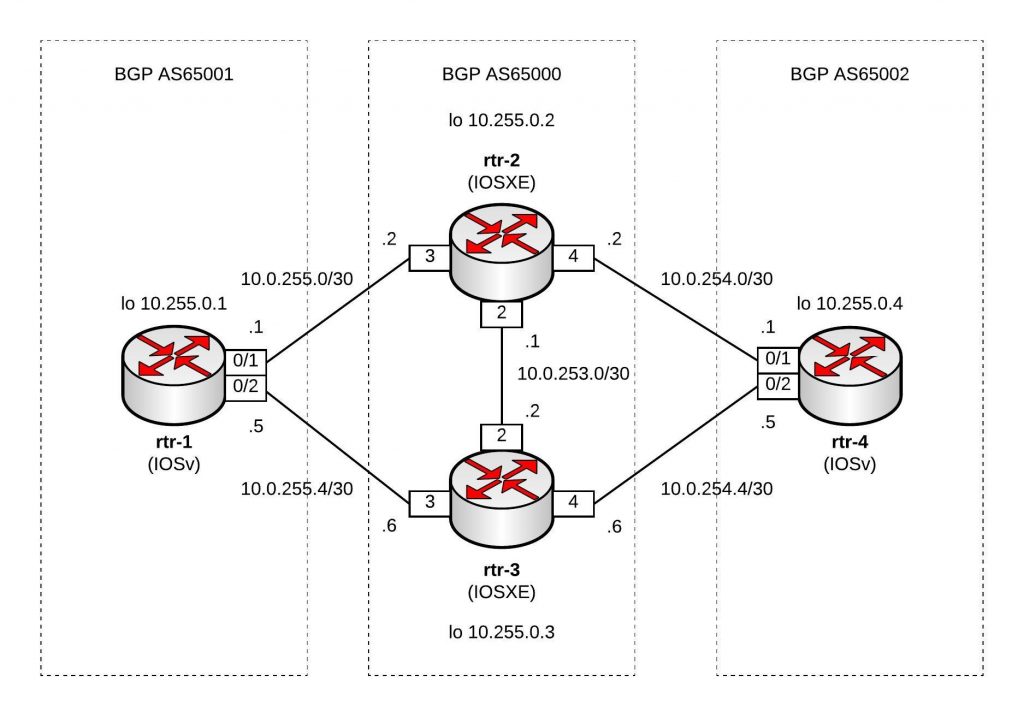
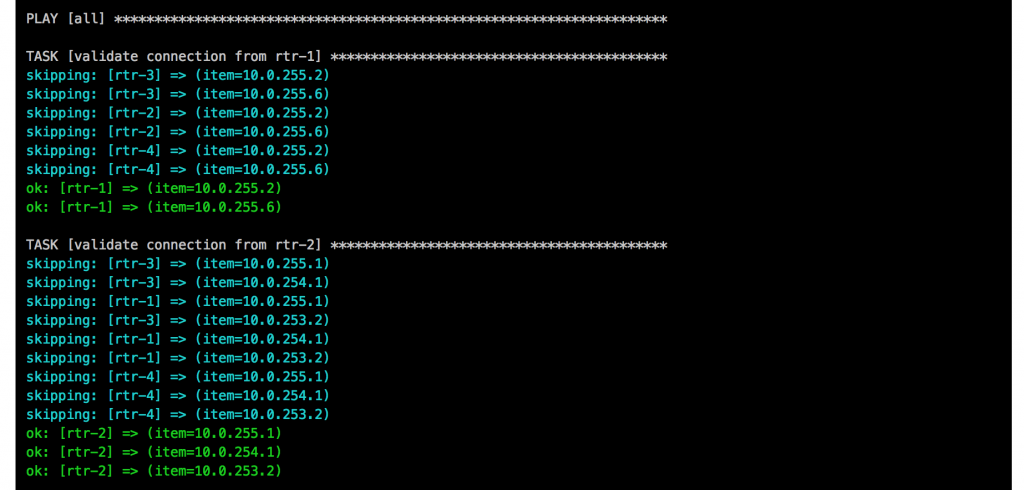
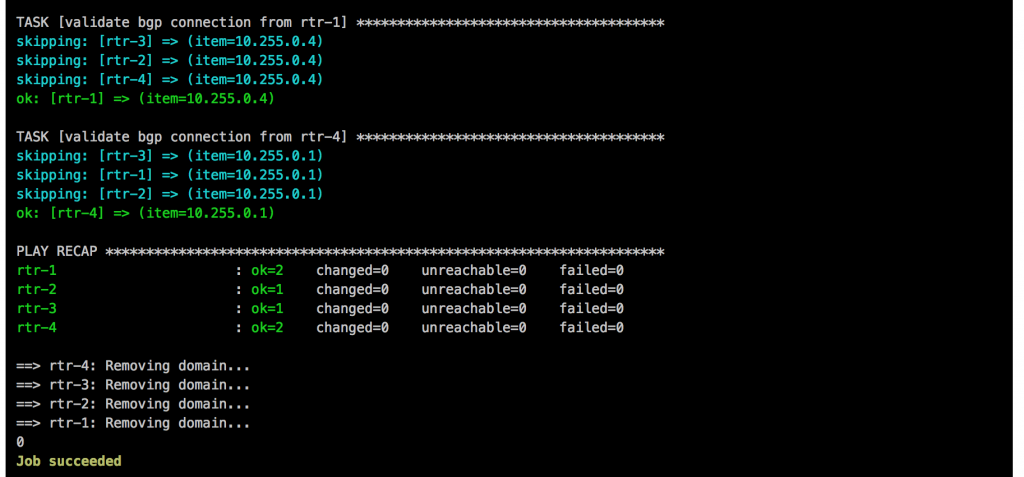
 I will continue to improve the Playbook and the CICD pipeline so come back later to check it out.
I will continue to improve the Playbook and the CICD pipeline so come back later to check it out.