The past few months I have been following the progress of the Kubernetes Cluster API which is part of the Kubernetes SIG (special interest group) Cluster-Lifecycle because they made good progress and wanted to try out the AWS provider version to deploy Kubeadm clusters. There are multiple infrastructure / cloud providers available which can be used, have a look at supported providers.
RedHat has based the Machine API Operator for the OpenShift 4 platform on the Kubernetes Cluster API and forked some of the cloud provider integrations but in OpenShift 4 this has a different use-case for the cluster to managed itself without the need of a central management cluster. I actually like RedHat’s concept and adaptation of the Cluster API and I hope we will see something similar in the upstream project.
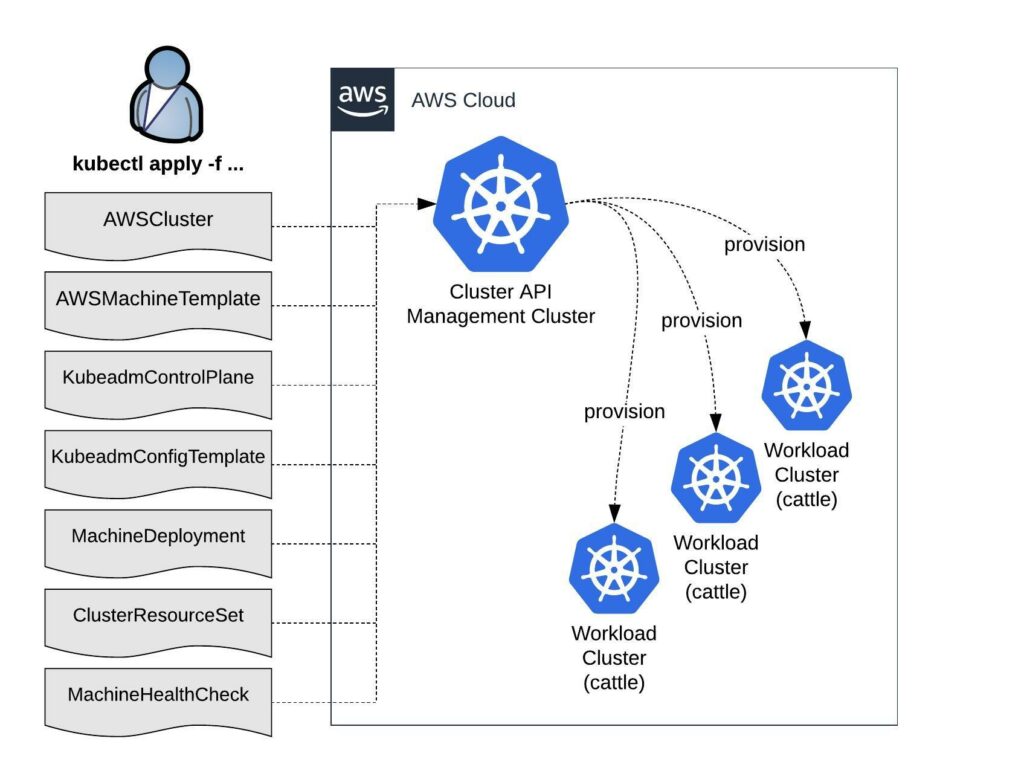
Bootstrapping workload clusters are pretty straight forward but before we can start with deploying the workload cluster we need a central Kubernetes management cluster for running the Cluster API components for your selected cloud provider. In The Cluster API Book for example they use a KinD (Kubernetes in Docker) cluster to provision the workload clusters.
To deploy the Cluster API components you need the clusterctl (Cluster API) and clusterawsadm (Cluster API AWS Provider) command-line utilities.
curl -L https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/cluster-api/releases/download/v0.3.14/clusterctl-linux-amd64 -o clusterctl chmod +x ./clusterctl sudo mv ./clusterctl /usr/local/bin/clusterctl curl -L https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/cluster-api-provider-aws/releases/download/v0.6.4/clusterawsadm-linux-amd64 -o clusterawsadm chmod +x ./clusterawsadm sudo mv ./clusterawsadm /usr/local/bin/clusterawsadm
Let’s start to prepare to initialise the management cluster. You need a AWS IAM service account and in my example I enabled the experimental features-gates for MachinePool and ClusterResourceSets before running clusterawsadm to apply the required AWS IAM configuration.
$ export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='<-YOUR-ACCESS-KEY->' $ export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY='<-YOUR-SECRET-ACCESS-KEY->' $ export EXP_MACHINE_POOL=true $ export EXP_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_SET=true $ clusterawsadm bootstrap iam create-cloudformation-stack Attempting to create AWS CloudFormation stack cluster-api-provider-aws-sigs-k8s-io I1206 22:23:19.620891 357601 service.go:59] AWS Cloudformation stack "cluster-api-provider-aws-sigs-k8s-io" already exists, updating Following resources are in the stack: Resource |Type |Status AWS::IAM::InstanceProfile |control-plane.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io |CREATE_COMPLETE AWS::IAM::InstanceProfile |controllers.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io |CREATE_COMPLETE AWS::IAM::InstanceProfile |nodes.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io |CREATE_COMPLETE AWS::IAM::ManagedPolicy |arn:aws:iam::552276840222:policy/control-plane.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io |CREATE_COMPLETE AWS::IAM::ManagedPolicy |arn:aws:iam::552276840222:policy/nodes.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io |CREATE_COMPLETE AWS::IAM::ManagedPolicy |arn:aws:iam::552276840222:policy/controllers.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io |CREATE_COMPLETE AWS::IAM::Role |control-plane.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io |CREATE_COMPLETE AWS::IAM::Role |controllers.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io |CREATE_COMPLETE AWS::IAM::Role |nodes.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io |CREATE_COMPLETE
This might take a few minutes before you can continue and run clusterctl to initialise the Cluster API components on your Kubernetes management cluster with the option –watching-namespace where you can apply the cluster deployment manifests.
$ export AWS_B64ENCODED_CREDENTIALS=$(clusterawsadm bootstrap credentials encode-as-profile) WARNING: `encode-as-profile` should only be used for bootstrapping. $ clusterctl init --infrastructure aws --watching-namespace k8s Fetching providers Installing cert-manager Version="v0.16.1" Waiting for cert-manager to be available... Installing Provider="cluster-api" Version="v0.3.14" TargetNamespace="capi-system" Installing Provider="bootstrap-kubeadm" Version="v0.3.14" TargetNamespace="capi-kubeadm-bootstrap-system" Installing Provider="control-plane-kubeadm" Version="v0.3.14" TargetNamespace="capi-kubeadm-control-plane-system" Installing Provider="infrastructure-aws" Version="v0.6.3" TargetNamespace="capa-system" Your management cluster has been initialized successfully! You can now create your first workload cluster by running the following: clusterctl config cluster [name] --kubernetes-version [version] | kubectl apply -f -
Now we have finished deploying the needed Cluster API components and are ready to create your first Kubernetes workload cluster. I go through the different custom resources and configuration options for the cluster provisioning. This starts with the cloud infrastructure configuration as you see in the example below for the VPC setup. You don’t have to use all three Availability Zone and can start with a single AZ in a region.
---
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: AWSCluster
metadata:
name: cluster-1
namespace: k8s
spec:
region: eu-west-1
sshKeyName: default
networkSpec:
vpc:
cidrBlock: "10.0.0.0/23"
subnets:
- availabilityZone: eu-west-1a
cidrBlock: "10.0.0.0/27"
isPublic: true
- availabilityZone: eu-west-1b
cidrBlock: "10.0.0.32/27"
isPublic: true
- availabilityZone: eu-west-1c
cidrBlock: "10.0.0.64/27"
isPublic: true
- availabilityZone: eu-west-1a
cidrBlock: "10.0.1.0/27"
- availabilityZone: eu-west-1b
cidrBlock: "10.0.1.32/27"
- availabilityZone: eu-west-1c
cidrBlock: "10.0.1.64/27"
Alternatively you can also provision the workload cluster into an existing VPC, in this case your cloud infrastructure configuration looks slightly different and you need to specify VPC and subnet IDs.
---
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: AWSCluster
metadata:
name: cluster-1
namespace: k8s
spec:
region: eu-west-1
sshKeyName: default
networkSpec:
vpc:
id: vpc-0425c335226437144
subnets:
- id: subnet-0261219d564bb0dc5
- id: subnet-0fdcccba78668e013
...
Next we define the Kubeadm control-plane configuration and start with the AWS Machine Template to define the instance type and custom node configuration. Then follows the Kubeadm control-plane config referencing the machine template and amounts of replicas and Kubernetes control-plane version:
---
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: AWSMachineTemplate
metadata:
name: cluster-1
namespace: k8s
spec:
template:
spec:
iamInstanceProfile: control-plane.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io
instanceType: t3.small
sshKeyName: default
---
apiVersion: controlplane.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: KubeadmControlPlane
metadata:
name: cluster-1-control-plane
namespace: k8s
spec:
infrastructureTemplate:
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: AWSMachineTemplate
name: cluster-1-control-plane
kubeadmConfigSpec:
clusterConfiguration:
apiServer:
extraArgs:
cloud-provider: aws
controllerManager:
extraArgs:
cloud-provider: aws
initConfiguration:
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
cloud-provider: aws
name: '{{ ds.meta_data.local_hostname }}'
joinConfiguration:
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
cloud-provider: aws
name: '{{ ds.meta_data.local_hostname }}'
replicas: 1
version: v1.20.4
We continue with the data-plane (worker) nodes which also starts with the AWS machine template, additionally we need a Kubeadm Config Template and then the Machine Deployment for the worker nodes with a number of replicas and used Kubernetes version.
---
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: AWSMachineTemplate
metadata:
name: cluster-1-data-plane-0
namespace: k8s
spec:
template:
spec:
iamInstanceProfile: nodes.cluster-api-provider-aws.sigs.k8s.io
instanceType: t3.small
sshKeyName: default
---
apiVersion: bootstrap.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: KubeadmConfigTemplate
metadata:
name: cluster-1-data-plane-0
namespace: k8s
spec:
template:
spec:
joinConfiguration:
nodeRegistration:
kubeletExtraArgs:
cloud-provider: aws
name: '{{ ds.meta_data.local_hostname }}'
---
apiVersion: cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: MachineDeployment
metadata:
name: cluster-1-data-plane-0
namespace: k8s
spec:
clusterName: cluster-1
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels: null
template:
metadata:
labels:
"nodepool": "nodepool-0"
spec:
bootstrap:
configRef:
apiVersion: bootstrap.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: KubeadmConfigTemplate
name: cluster-1-data-plane-0
clusterName: cluster-1
infrastructureRef:
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: AWSMachineTemplate
name: cluster-1-data-plane-0
version: v1.20.4
A workload cluster can be very easily upgraded by changing the .spec.version in the MachineDeployment and KubeadmControlPlane configuration. You can’t jump over a Kubernetes versions and can only upgrade to the next available version example: v1.18.4 to v1.19.8 or v1.19.8 to v1.20.4. See the list of supported AMIs and Kubernetes versions for the AWS provider.
At the beginning we enabled the feature-gates when we were initialising the management cluster to allow us to use ClusterResourceSets. This is incredible useful because I can define a set of resources which gets applied during the provisioning of the cluster. This only get executed one time during the bootstrap and will be not reconciled afterwards. In the configuration you see the reference to two configmaps for adding the Calico CNI plugin and the Nginx Ingress controller.
---
apiVersion: addons.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: ClusterResourceSet
metadata:
name: cluster-1-crs-0
namespace: k8s
spec:
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name: cluster-1
resources:
- kind: ConfigMap
name: calico-cni
- kind: ConfigMap
name: nginx-ingress
Example of the two configmaps which contain the YAML manifests:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: calico-cni
namespace: k8s
data:
calico.yaml: |+
---
# Source: calico/templates/calico-config.yaml
# This ConfigMap is used to configure a self-hosted Calico installation.
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: calico-config
namespace: kube-system
...
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
deploy.yaml: |+
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
...
Without ClusterResourceSet you would need to manually apply the CNI and ingress controller manifests which is not great because you need the CNI plugin for all nodes to go into Ready state.
$ kubectl --kubeconfig=./cluster-1.kubeconfig apply -f https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.15/manifests/calico.yaml
$ kubectl --kubeconfig=./cluster-1.kubeconfig apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v0.41.2/deploy/static/provider/aws/deploy.yaml
Finally after we have created the configuration of the workload cluster we can apply cluster manifest with the option for setting custom clusterNetwork and specify with service and pod IP range.
---
apiVersion: cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: cluster-1
namespace: k8s
labels:
cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name: cluster-1
spec:
clusterNetwork:
services:
cidrBlocks:
- 172.30.0.0/16
pods:
cidrBlocks:
- 10.128.0.0/14
controlPlaneRef:
apiVersion: controlplane.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: KubeadmControlPlane
name: cluster-1-control-plane
infrastructureRef:
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: AWSCluster
name: cluster-1
The provisioning of the workload cluster will take around 10 to 15 mins and you can follow the progress by checking the status of different configurations we have applied previously.
You can scale both Kubeadm control-plane and MachineDeployment afterwards to change the size of your cluster. MachineDeployment can be scaled down to zero to save cost.
$ kubectl scale KubeadmControlPlane cluster-1-control-plane --replicas=1 $ kubectl scale MachineDeployment cluster-1-data-plane-0 --replicas=0
After the provisioning is completed you can get kubeconfig of the cluster from the secret which got created during the bootstrap:
$ kubectl --namespace=k8s get secret cluster-1-kubeconfig -o jsonpath={.data.value} | base64 --decode > cluster-1.kubeconfig
Example check the node state.
$ kubectl --kubeconfig=./cluster-1.kubeconfig get nodes
When your cluster is provisioned and nodes are in Ready state you can apply the MachineHealthCheck for the data-plane (worker) nodes. This automatically remediate unhealthy nodes and provisions new nodes to join them into the cluster.
---
apiVersion: cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: MachineHealthCheck
metadata:
name: cluster-1-node-unhealthy-5m
namespace: k8s
spec:
# clusterName is required to associate this MachineHealthCheck with a particular cluster
clusterName: cluster-1
# (Optional) maxUnhealthy prevents further remediation if the cluster is already partially unhealthy
maxUnhealthy: 40%
# (Optional) nodeStartupTimeout determines how long a MachineHealthCheck should wait for
# a Node to join the cluster, before considering a Machine unhealthy
nodeStartupTimeout: 10m
# selector is used to determine which Machines should be health checked
selector:
matchLabels:
nodepool: nodepool-0
# Conditions to check on Nodes for matched Machines, if any condition is matched for the duration of its timeout, the Machine is considered unhealthy
unhealthyConditions:
- type: Ready
status: Unknown
timeout: 300s
- type: Ready
status: "False"
timeout: 300s
I hope this is a useful article for getting started with the Kubernetes Cluster API.